Understanding Osteoporosis ICD-10 Code: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog is about Osteoporosis and understanding Osteoporosis ICD-10 Code, Osteoporosis is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects the bones. In the medical field, proper coding and classification of diseases and conditions are crucial for accurate documentation and billing. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), provides a standardized system for coding various health conditions, including osteoporosis. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of osteoporosis, its ICD-10 code, implications, and management.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Osteoporosis
2. Significance of ICD-10 Coding
3. Osteoporosis ICD-10 Code Explained
4. Understanding Bone Health
5. Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
6. Diagnostic Procedures
7. Complications of Untreated Osteoporosis
8. Lifestyle Modifications for Stronger Bones
9. Pharmacological Interventions
10. Role of Nutrition in Osteoporosis Management
11. Exercises for Bone Health
12. Building Bone Density in Different Life Stages
13. Importance of Regular Check-ups
14. Raising Awareness about Osteoporosis
15. Conclusion
Introduction to Osteoporosis ICD 10
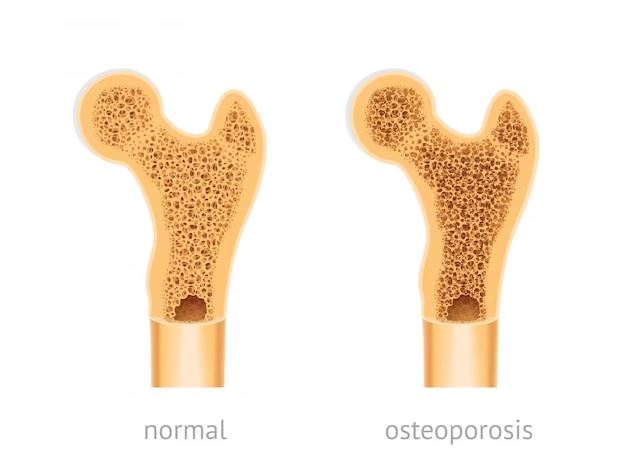
Osteoporosis is a medical condition in which the bones become weakened, making them more prone to fractures and breaks. Often referred to as the “silent disease,” osteoporosis develops gradually and can remain undetected until a fracture occurs. It predominantly affects older adults, especially women after menopause, due to the decrease in estrogen levels. However, it can also affect men and younger individuals.
Significance of ICD-10 Coding
ICD-10 codes are essential for accurate medical documentation, billing, and statistical purposes. They provide a standardized way to classify and identify health conditions, enabling healthcare providers and insurance companies to understand the diagnosis and treatment required. Proper coding ensures streamlined communication among medical professionals and accurate reimbursement for services rendered.
Osteoporosis ICD-10 Code Explained
The ICD-10 code for osteoporosis is M81.0. This code falls under the category of “Disorders of Bone Density and Structure.” The M81.0 code is used to specify primary osteoporosis and is further divided based on the site of the fracture, such as vertebrae, femur, or other bones. Proper coding helps in specifying the severity and location of the condition, which aids in tailoring appropriate treatment plans.
Understanding Bone Health For
Osteoporosis ICD-10
Bones are dynamic structures that undergo a constant process of remodeling. This involves the breaking down of old bone tissue and the formation of new bone. Calcium and other minerals are important for bone health. A balance between bone resorption and formation is necessary to maintain bone density and strength.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis ICD-10
Several risk factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. These include genetics, hormonal changes, low calcium intake, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions. Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and prevention of the condition.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing osteoporosis involves assessing bone mineral density (BMD). Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is a commonly used method to measure BMD at various skeletal sites. The T-score obtained from DXA helps in determining the presence and severity of osteoporosis.
Complications of Untreated Osteoporosis (ICD-10)
Untreated osteoporosis can lead to severe complications, such as fractures, chronic pain, reduced mobility, and decreased quality of life. Fractures, especially in the spine and hip, can result in long-term disability and increased mortality rates among older adults.
Lifestyle Modifications for Stronger Bones
Lifestyle changes play a significant role in managing and preventing osteoporosis. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular weight-bearing exercises, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, and fall prevention strategies are essential for maintaining bone health.
Pharmacological Interventions
In cases where lifestyle modifications are insufficient, healthcare providers may recommend pharmacological interventions. Medications such as bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and denosumab aim to increase bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
Role of Nutrition in Osteoporosis Management
A balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, protein, magnesium, and other nutrients is vital for bone health. Dairy products, leafy greens, fish, nuts, and fortified foods can contribute to maintaining strong bones.
Exercises for Bone Health
Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, dancing, and resistance training promote bone strength. These activities stimulate bone remodeling and enhance bone density.
Building Bone Density in Different Life Stages
Bone density can be optimized at various life stages, starting from childhood and adolescence. Maximizing peak bone mass during youth and preserving it in adulthood through proper nutrition and physical activity is crucial.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups facilitate early detection of bone density changes and osteoporosis risk factors. Timely interventions can prevent the progression of the condition.
Raising Awareness about Osteoporosis (ICD-10)
Creating awareness about osteoporosis and its prevention is essential. Educating the public about risk factors, diagnostic methods, and lifestyle modifications can lead to better bone health and reduced incidence of fractures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the osteoporosis ICD-10 code and its implications is vital for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this bone-weakening condition. By implementing lifestyle changes, seeking timely medical advice, and spreading awareness, we can ensure stronger bones and improved quality of life for individuals at risk of osteoporosis.
FAQs
1. What is the ICD-10 code for osteoporosis?
A. The ICD-10 code for osteoporosis is M81.0, specifying primary osteoporosis and its location.
2. Who is at risk for developing osteoporosis?
A. Older adults, especially women after menopause, and individuals with low calcium intake or certain medical conditions are at higher risk.
3. How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
A. Osteoporosis is diagnosed through a bone mineral density test, commonly using DXA scans.
4. Can osteoporosis be prevented?
A. Yes, osteoporosis can be prevented through a combination of a balanced diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications.
5. What are the complications of untreated osteoporosis?
A. Untreated osteoporosis can lead to fractures, chronic pain, reduced mobility, and decreased quality of life.
6. what is the best and safest treatment for osteoporosis?
A. The best and safest osteoporosis treatment varies but typically includes a combination of exercise, calcium/vitamin D intake, and medications prescribed by a healthcare professional.
7. how to treat osteoporosis without medication?
A. Treating osteoporosis without medication can involve exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and lifestyle changes
8. what is the safest osteoporosis drug?
A. Bisphosphonates and denosumab were among the commonly prescribed safer osteoporosis drugs, but consult a medical professional for personalized advice.
